Understanding Waist Circumference and Abdominal Fat: Health Risks and Management
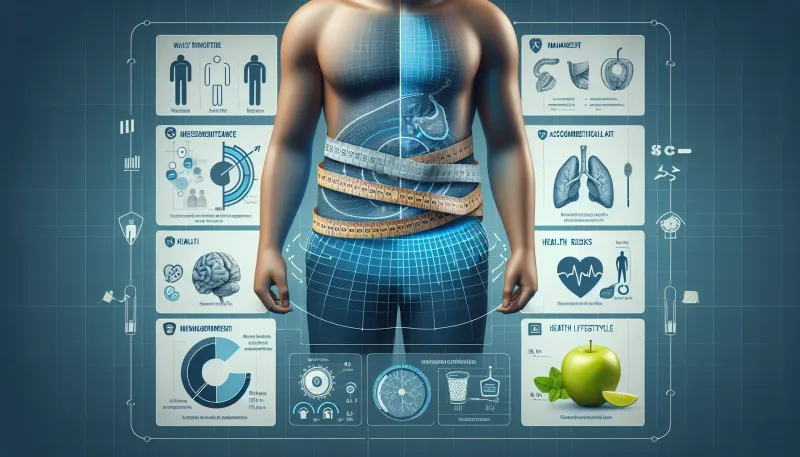
Learn about the health risks of waist circumference and abdominal fat, and discover effective management strategies to improve your wellness.
Introduction
In recent years, researchers and healthcare professionals have emphasized the importance of maintaining a healthy waist circumference. This metric, indicative of abdominal fat, serves as a significant risk factor for several chronic conditions. Understanding the relationship between waist circumference and abdominal fat can help you take proactive steps towards healthier living.
What is Waist Circumference?
Waist circumference measures the distance around the smallest area of the waist, typically found between the bottom of the rib cage and the top of the hips. This simple yet effective measure helps estimate abdominal fat levels, distinguishing between subcutaneous fat (under the skin) and visceral fat (around internal organs).
How to Measure Waist Circumference
To measure your waist circumference:
- Use a flexible, non-stretchable tape measure.
- Stand upright and wrap the tape measure around your waist, at the narrowest point.
- Ensure the tape is snug but not compressing the skin, and measure at the end of a normal exhalation.
Health Risks of Excess Abdominal Fat
Abdominal fat, especially visceral fat, poses greater health risks compared to fat stored in other areas. Here are some significant health concerns associated with excess abdominal fat:
Cardiovascular Diseases
Excess abdominal fat increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack and stroke. Visceral fat contributes to heightened levels of inflammation and insulin resistance, both critical factors in heart disease development.
Type 2 Diabetes
Individuals with larger waist circumferences are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Visceral fat adversely affects insulin sensitivity, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and, ultimately, diabetic conditions.
Certain Cancers
Higher amounts of abdominal fat correlate with an increased risk of certain cancers, such as colorectal and breast cancer. The underlying mechanisms involve hormonal alterations and inflammatory processes driven by excess visceral fat.
Fatty Liver Disease
Excessive abdominal fat can lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver, causing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). This condition can progress to liver inflammation, fibrosis, and even cirrhosis if left unmanaged.
Managing Waist Circumference and Abdominal Fat
Reducing abdominal fat is achievable with a combination of lifestyle modifications, including diet, exercise, and behavioral changes. Here are some effective strategies:
Adopt a Healthy Diet
Focus on a balanced, nutrient-dense diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Reducing intake of processed foods, sugar, and trans fats can significantly impact abdominal fat reduction.
Fiber-Rich Foods
Consuming plenty of fiber aids in stabilizing blood sugar levels and promotes satiety, making it easier to manage your waistline. Foods high in soluble fiber, such as oats, flaxseeds, and legumes, are particularly beneficial.
Protein Intake
Adequate protein consumption helps build lean muscle mass and boosts metabolism, facilitating fat loss. Incorporate sources like fish, poultry, beans, and dairy into your daily meals.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise is crucial for burning calories and reducing abdominal fat. Combine aerobic exercises, such as walking, running, or swimming, with strength training to optimize fat loss and enhance overall fitness.
Core Strengthening
Including exercises that target core muscles, such as planks, bicycle crunches, and leg raises, can help tone the abdominal area and improve waist circumference.
Behavioral Modifications
Implementing small yet impactful lifestyle changes can help sustain waistline management:
- Prioritize adequate sleep to regulate hunger hormones and prevent weight gain.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Consistently monitor your waist circumference to track progress and stay motivated.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of waist circumference and its relation to abdominal fat is crucial for monitoring and maintaining overall health. By recognizing the health risks associated with excess abdominal fat and adopting effective management strategies, you can take charge of your wellbeing. Implementing a combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications will significantly contribute to a healthier waistline and better health outcomes.